Aquatic Biomes
Edited by R Ellis, Jen Moreau, Sharingknowledge, SarMal
Biomes
Biomes are distinct ecosystems classified by climate, vegetation, and animal life. Aquatic biomes are in the water. Terrestrial biomes are on land. Organisms in biomes obtain nutrients from many sources, such as soils, decaying vegetation and animals, and lower trophic levels. Human and environmental interactions alter characteristics of biomes, including their future fate. There are 5 main categories of biomes: aquatic, deserts, forests, grasslands, and tundra.
Aquatic biome
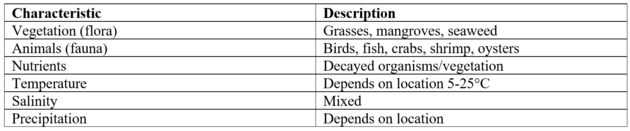
The aquatic biome includes saltwater and freshwater. Characteristics of the aquatic biome vary greatly, depending on salinity, depth, area, and location. Freshwater areas include surface waters and wetlands. Saltwater marine waters include oceans, marshes, estuaries, and coral reef (in oceans).
Saltwater
Estuaries
Estuaries are regions where oceans meet freshwater influent from streams and rivers. Salinity gradients in estuaries create zones with different organisms. Like wetlands, there is a rich diversity of organisms.
Oceans
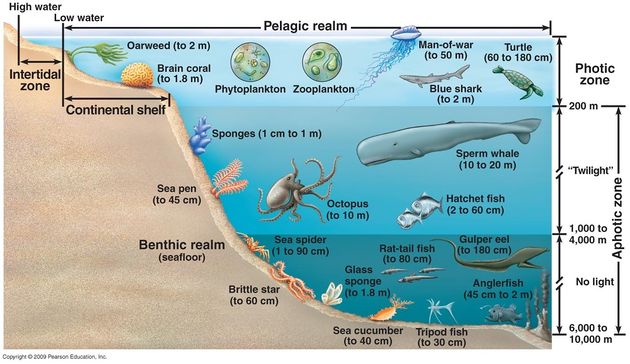
Oceans are the largest biome on Earth. There are five oceans, Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern (Antarctic). Oceans are generally cold, but ocean currents mix some warmer waters to deeper sections of the water column. There are different zones in oceans named according to an approximate depth from deepest to most shallow: abyssal, benthic, pelagic, and intertidal. Different organisms tend to thrive in different zones. The abyssal zone is the very deepest of ocean bottoms. There is high water pressure, temperatures close to 3°C, and chemolithoautotrophs near hydrothermal vents, These bacteria act as a food source for invertebrates. The benthic zone is the bottom of the ocean (less deep), is home to sponges, sea anemone, sea stars, and fish. The pelagic zone is above the benthic zone and is home to seaweed, dolphins, whales, and fish. The pelagic zone includes seaweed, fish, and dolphins. The intertidal zone is where the ocean and land touch. Organisms here must adjust to changing water levels and wave action constantly. Wave action reduces vegetated areas to algae and grasses. The intertidal zone is where mollusks, clams, worms, crabs, and fish flourish.
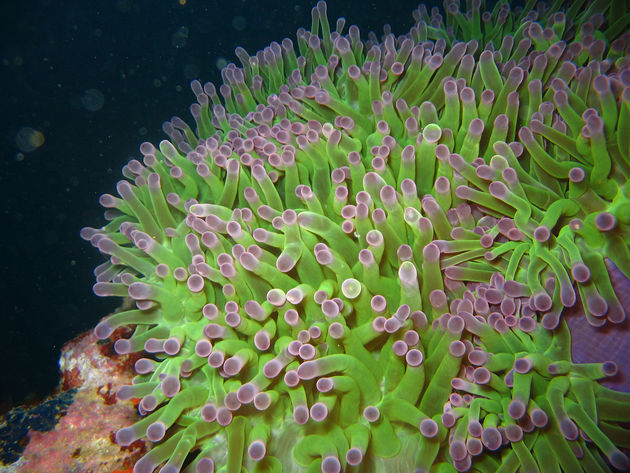
Coral Reefs
Coral reefs prevail in shallow oceans with mild temperature. Corals are made of animal polyps and algae. They extend tentacles to trap plankton for nutrients. This ecosystem is one of the richest diversities of the different biomes. The Great Barrier Reef off Australia's coast is probably the most famous coral reef.
Freshwater
Ponds, lakes, rivers
Ponds, lakes, and rivers that are deep may have temperature gradients that mix more often during spring and fall. Any waters that reach over 35° begin to stress and kill fish. Vegetation usually lines these areas, known as riparian buffers. This could include shrubbery and trees. The vegetation must be able to thrive in constant water. The longest river in the world is the Amazon River.
Wetlands
Wetlands are shallow areas containing water at least 6 months per year. This creates a hydric soil, which is an identifying feature of wetlands. Hydrophytic vegetation is the last characteristic indicating a wetland's presence. Water may be saltwater or freshwater, depending on location. Saltwater wetlands are termed marshes. These are some of the most diverse areas on the planet. Approximately 6% of the earth is covered by wetlands.
Sources
Blueplanetbiomes.org. http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/world_biomes.htm
Delanie. All about the ocean. http://allaboutoceanmrvarney.weebly.com/8.html
N.A. https://sites.google.com/site/climatetypes/arid
University of Berkeley. Biomes. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/glossary/gloss5/biome/index.html
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Aquatic Biomes. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 25, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/Aquatic_Biomes
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Aquatic Biomes." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/Aquatic_Biomes Accessed 25 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Aquatic Biomes." Accessed Apr 25, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/Aquatic_Biomes.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Hydrology
Recent edits by: Sharingknowledge, Jen Moreau, R Ellis