Artificial Intelligence
Edited by Jen Moreau
- 1 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
- 2 HISTORY OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT
- 3 INTELLIGENT
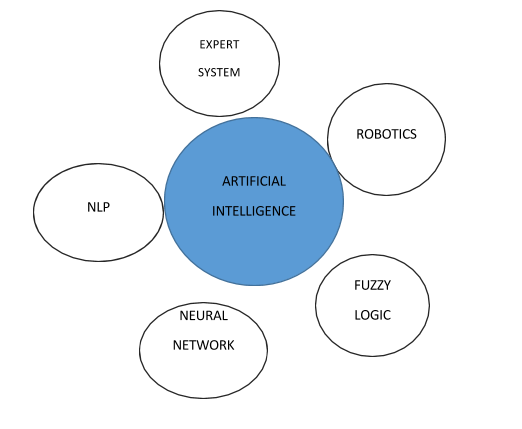
- 4 COMPONENT OF AI
- 5 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HUMAN AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
- 6 RESEARCH AREAS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT
- 7 AGENTS AND ENVIRONMENTS
- 8 TYPES OF AGENT
- 9 TERMINOLOGY IN AGENTS
- 10 RATIONALITY
- 11 RATIONALITY OF AN AGENT DEPENDS ON THE FOLLOWING
- 12 Referencing this Article
- 13 Comments
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Artificial intelligent is the branch of computer sciences that deals with making intelligent, decision-making machines that think the way humans do. This field of computer science studies the way human think, learn and make decisions then write a computer program that mimics the human reasoning faculty.
The philosophy behind the invention of Artificial Intelligent stems from the curiosity of man to develop a machine that reasons and acts the way humans do. This led to the development of the field of Artificial Intelligent.
When AI was developed they have several goals, some of which are listed below.
- To implement machine that mimics human Intelligent:
- To develop Expert system
Many disciplines contributed greatly to the development of Artificial
- Intelligent
- Computer Science
- Mathematics
- Sociology
- Philosophy
- Psychology
- Biology
- Neuroscience
- Economics
- Computer engineering
- linguistics
There are different fields were the knowledge of AI is hugely employed such as;
Gaming: Artificial Intelligent plays a vital role in coding of most strategic games like poker, draft, chess etc
Expert Systems: Expert systems provide explanation and advice with the help of an integrated machine, software and knowledge base. AI plays a crucial role in the development of this field.
Natural Language Processing: AI contributes to the development of this field of programming language.
Vision Systems: These are built to understand, comprehend and interpret visual input
Speech recognition: Some intelligent systems are developed to be able to understand and interpret human speeches. It can also handle different slang, accents etc.
Intelligent Robots: these are built to be able to handle a task that is supposed to be done by a human. They have efficient processors, multiple sensors, and a huge memory.
HISTORY OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT
- 1923: The first use of the term robot was by Karel Capek in his played "Rossum's Universal Robots".
- 1943: the foundation of neural networks was laid.
- 1945: the word ROBOTICS was coined by Isaac Asimov
- 1950: Turing Test was introduced to evaluate intelligence of a machine; by Alan Turing
- 1956: the term Artificial Intelligence was coined by John McCarthy.
- 1958: Lisp programming language for AI was invented by JOHN McCarthy
- 1964: Danny Bobrow's displayed that computers can understand natural language.
- 1965: ELIZA was built.
- 1969: SHAKEY, a robot equipped with locomotion and problem-solving.
- 1973: FREDDY was built, a Scottish Robot capable of using vision to locate and assemble models.
- 1979: STANFORD CART; the first computer-controlled autonomous vehicle.
- 1985: AARON; a drawing program was demonstrated by Harold Cohen
- 1990: this year mark the major advances in the field of AI: Scheduling, Cased-based reasoning, multi=agent planning, and virtual reality.
- 1997: the Deep blue chess program beats the then World chess Champion
- 2000: the robot NOMAD explores remote regions of Antarctic.
INTELLIGENT
This is the ability for a system to calculate, learn from experiences, reason, store and retrieve information and other cognitive abilities of a human.
There are different types of intelligent system, below are some examples:
Linguistic Intelligence: this is the ability for a system to speak, recognize and use mechanisms and semantics.
Logical- mathematical intelligent: the ability to use and understand complex and abstract ideas.
Intra- [personal Intelligent: it is the ability to differentiate between our own personal feelings and intentions.
Interpersonal Intelligent: it is the ability to differentiate among other people feelings and intentions.
COMPONENT OF AI
- REASONING: it is the ability to conduct basis for decisions, prediction, and judgments.
- LEARNING: it is gaining knowledge or skills by means of experience, reading, practicing and studying.
- PROBLEM-SOLVING: it is the ability to resolve a conclusion or make a decision that elevates or provide a solution to a known or unknown hurdles.
- PERCEPTION: it is the process of acquiring, organizing, interpreting sensory information
- LINGUISTIC INTELLIGENCE: it is the ability to speak, comprehend and understand verbal and written language.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HUMAN AND MACHINE INTELLIGENCE
- Humans can figure out an object even though it is not complete, but machines cannot.
- Humans perceive things by patterns, but machine by rules and data.
- Human recall by pattern but the machine does it by searching algorithm.
RESEARCH AREAS OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENT
Speech and Voice Recognition: both terms are often used interchangeably, there is a striking difference between them. Speech recognition aims at comprehending and understanding what was spoken while voice recognition recognizes who is speaking. In the speech, recognition machine does not need to be trained specifically as it is not speaker dependent while Voice recognition system needs training specifically.
AGENTS AND ENVIRONMENTS
An agent is anything that can perceive the immediate environment through sensors and act upon through defectors.
TYPES OF AGENT
Human Agent: this has all human sensorial, such as eyes, ears, nose, tongue etc.
Robotic Agent: used as cameras and various motors and also actuators for defectors.
Software Agent: encoded with bit strings as its programs and action.
TERMINOLOGY IN AGENTS
Performance Measure of Agent: it is a criterion used to determine the success rate of an agent.
The behavior of Agent: this is the action performed by an agent after a sequence of precepts.
Precepts: it is referred as the perceptual inputs at a given time.
Precept Sequence: it is the stored history of agent perception.
Agent Function: it is the map from precept sequence to action.
RATIONALITY
Rationality has to do with being sensible, reasonable and having a great sense of judgment. It is concerned with expected reaction depending on what is perceived by the agent. It performs actions with the purpose of getting information.
RATIONALITY OF AN AGENT DEPENDS ON THE FOLLOWING
- Performance measure: determines the degree of success
- Agents Precept Sequence
- Agents prior knowledge on the environment
- Actions the agent can perform
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Artificial Intelligence. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 23, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/Artificial_Intellegence
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Artificial Intelligence." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/Artificial_Intellegence Accessed 23 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Artificial Intelligence." Accessed Apr 23, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/Artificial_Intellegence.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Computational Linguistics