Category:Electricity
Electricity is a type of energy used everywhere in society.
Mains Electricity
A plug's components (live, neutral, earth wire; fuse) and how to wire it. Double insulation and circuit breakers. The volt equation: power current and voltage and how this could be used to calculate electricity bills. See Mains Electricity
Energy Efficiency
Types of energy (thermal, light, kinetic, chemical, nuclear, potential). What is energy efficiency and how it can be calculated. How home insulation works to reduce energy loss by example of cavity wall and double glazing. See Energy Efficiency
Electromagnetism
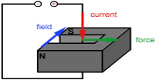
The use of electrical current to produce a magnetic field: the electric motor. Electromagnetic induction and how this is used in transformers to increase or decrease voltage in energy supply. See Electromagnetism
Electricity Generation
The importance of generating electricity and the implications. The difference between renewable and non-renewable sources. Different types of electricity generation: nuclear, coal, oil, wind turbines. See Electricity Generation
Current
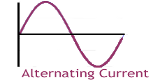
In a solid metal conductor, current is the flow of free electrons (negatively charged) which move from negative to positive. Creating an overall movement of charge in this direction. Direct and alternating current (AC or DC). See Current
Charge
An atom has a positively and negatively charged portion. Electrical conductors vs insulators. Electrostatic phenomena (static electricity) and its practical applications in industry and the importance of earthing in some circumstances. See Charge
Electrical Circuits
Parallel circuits have junctions and are used in Christmas lights for instance. Series circuits is simpler. Ohm's law providing a relationship between voltage, current and resistance (measured in ohms). See Electrical Circuits
How to articles in category "Electricity"
The following 8 pages are in this category, out of 8 total.