Introduction to Psychology
Edited by Shelleymarie, Jen Moreau
Psychology is derived from the Greek words psyche (spirit, soul) and logos (knowledge, study). When combined, the words mean knowledge about spirit or soul, mental process and behavior.
Psychology is defined as a scientific study of behavior and mental processes and a Psychologist is the person who provides guidance or consolation to an individual through help in different forms therapy. Therapy is an meeting to which the Psychologist conducts thorough observations, practices, and experiments to find the best outcome for the patient.
- 1 Performing Scientific Research
- 2 Research Methods in Psychology
- 3 Observation Research Method
- 4 Interview Method
- 5 Experimental Method
- 6 Survey Method
- 7 Tools of Survey
- 8 Case History Method
- 9 Fields of Psychology
- 10 This article is part of a series on 'Introduction to Psychology'. Read the other articles here:
- 11 Referencing this Article
- 12 Comments
Performing Scientific Research
In this step of therapy, there are 6 steps to which a Psychologist will review, to assess the issues that need to be addressed for the patient.
Identify the problem or research topic. For example, the impact of sleep disturbance on test performance. Review related literature from the abundant amount of resources provided.
Formulation of hypothesis. For example, different assumptions, either positive and negative before any task. It can be null also.
Conduct research. There are many ways this can be done, either by content analysis, questionnaire, case study, lab experiments, correlation, Interview, field work, observation.
Analyze the results. Such as using software used for logical and non--logical batched statistical analysis called SPSS.
Conclusion. What is your end result and the best outcome? Either our research is rejected or accepted.
Research Methods in Psychology
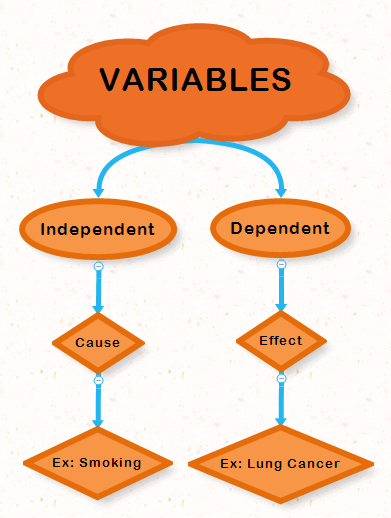
There are many different ways to conduct research in psychology, you use the methods and tools that work best in the situation that you are trying to review. There are also variables that need to be considered. A variable is a thing that should be changed, either quality or quantity. There are two types of variables.
Some of the most common types of research are as follows:
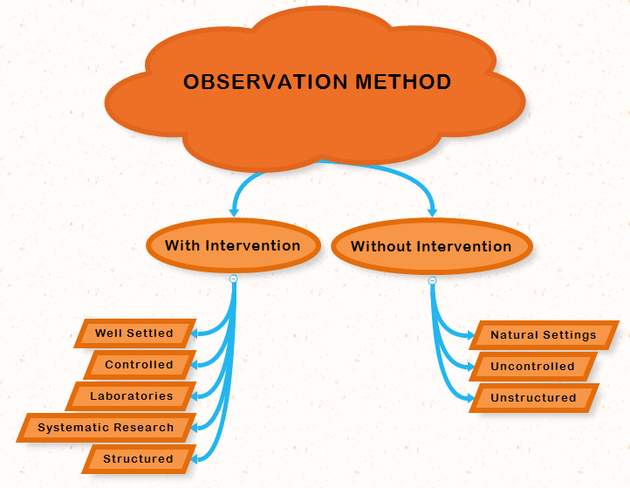
Observation Research Method
In this method of observing a person who will be treated, can be done in two different ways. Overt behavior is when the patient knows they're being observed. Covert behavior is when the person doing the research pretends to be part of a gathering and doing their observations, but this method can be considered to be a problem with deception and an ethically a problem with personal privacy.
Interview Method
Interviews are conducted in person and on a more personal basis which is face to face. This method allows the psychologist to obtain relevant information for research, and it can help the interviewer gather more detailed information behind the individual's experience. Now this can be done in one of two different processes.
Experimental Method
Key Features
- Control over variables
- Establishing cause and effect relationship
There are three types of experimental methods:
- Control experiments, laboratory
- Field experiments, as a participant
- Natural experiments, natural settings
Survey Method
This method is for collecting information to do research on different people's attitude, opinions and suggestions on a written paper, involving a large number of people.
Steps of Survey
Formulation of the problem. Here we identify the problem, topic of survey or title. This helps to establish the survey's information needs, operational definitions, topics of address and the analysis plan. It determines what to include or exclude in the survey, such as what the client needs to know vs. what is not absolutely necessary. It should be concise and make your research problem clear to the audience. It's the core of your research process.
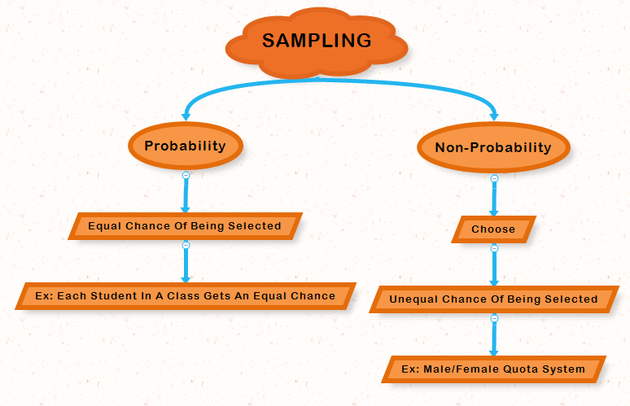
Population and Sampling. Population is the total population of people during the survey. Sampling is choosing people for research and experiments during the survey.
Tools of Survey
Data collection is an important aspect of any type of research study. If any information is incorrect, it can impact the results of the study and lead to invalid results. Most data collection is in the form of mail, questionnaires, interviews, telephone, etc. Here are a few examples of different questionnaires.
- Open-ended (having opinion)
- Closed-ended (simple yes or no)
Data analysis. SPSS software is used to analyze data.
Results. Once all the data has been collected and analysis, the psychologist can then make a hypothesis and a conclusion of the end results.
Case History Method
This method originated in clinical medicine. Before diagnosing a patient, gather all of the patient's personal and diagnostic history, such as depression, anxiety, etc. You can also use personal interviews, previous treatments, official documents such as clinical or case notes, the patient's memories, memories of the patient's friends or family members, photographs, writings and other aspects of the human experience to investigate and develop a diagnosis.
Fields of Psychology
There are several different fields or areas within the realm of psychology.
Educational psychology is one type of psychology that usually pertains to children in an educational setting. This type of psychology delves into how people retain knowledge and how learning methods affect cognitive development of the individual.
Social psychology is the study of social interaction, including its origin and its cognitive effect on the patient. It studies how the thoughts and feelings of people are affected by others, whether real or imagined.
Industrial psychology is the scientific study of human behavior in the workplace. This type applies the study of psychology to individuals or teams within organizations or businesses.
Developmental psychology is the study of psychology from an individual's birth until death. It studies how and why people change, grow and develop throughout their lifetime. Some of the observations that developmental psychologists take into account include changing physical appearances such as height, weight, etc., motor skills, cognitive development, self-concept, language, personality, ethics, and emotions.
Criminal psychology studies the thoughts, actions, motivations and reactions of individuals who partake in criminal behavior. Criminal psychologists often help solve crimes and develop criminal profiles.
Abnormal psychology involves studying patterns of abnormal or unusual behavior. Some aspects of abnormality include distress, deviation or dysfunction.
Clinical psychology focuses on diagnosing a wide range of emotional, mental and behavioral issues. It includes the study of learned behaviors and takes into account an individual's past and present case history, assessment, and treatment.
Counseling psychology focuses on the study of emotional, social, vocational, educational and organizational concerns in relation to personal and interpersonal functioning. There is no age limit for the patients, and counseling psychologists provide guidance and therapy related to daily life and conflicts.
This article is part of a series on 'Introduction to Psychology'. Read the other articles here:
1) Introduction_to_Psychology
3) Stages and Types of Learning
4) The Psycological Theory of Emotions
5) Nature and Psychology of Intelligence
6) Motivation
7) Personality
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Introduction to Psychology. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 20, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/Introduction_to_Psychology
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Introduction to Psychology." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/Introduction_to_Psychology Accessed 20 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Introduction to Psychology." Accessed Apr 20, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/Introduction_to_Psychology.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Psychology
Recent edits by: Shelleymarie