Types and Structure of Ribonucleic Acid
Edited by Jen Moreau, Marisha, SarMal, Sharingknowledge
Ribonucleic Acid
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule and like the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), is composed of nucleotides. Unlike DNA, RNA is a single stranded molecule with chain lengths ranging from 10 to more than 1000 nucleotides and serves various biological functions in an organism's cell. These functions include coding, decoding, carrying genetic information, regulation, and expression of genes in living organisms. A nucleotide is the building block of ribonucleic acid; consisting of three sub-units: nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
While proteins are widely known to be responsible for catalysis in cells, some RNA also play crucial roles as catalysts in biological reactions. For example, ribozyme catalyzes chemical reactions in a similar fashion as protein enzymes.
There are three main characteristics that distinguish RNA from other types of nucleic acids:
- 1An example of an RNA complementary pairing is HIV viral RNA. Once the virus enters the host cell, HIV viral RNA is converted to a double-stranded RNA by the enzyme 'reverse transcriptase.'RNA is a single-stranded molecule, however, it can form a double-stranded molecule through complementary pairing.Advertisement
- 2Ribose has a hydroxyl group (OH) on the 2' carbon and deoxyribose does not. Deoxy stands for the lack of one oxygen atom that is present in ribose sugar, making deoxyribose more stable than ribose.The sugar on the RNA molecule contains a ribose sugar on its backbone.
- 3Purines are composed of adenine (A) and guanine (G), while pyrimidines are made up of cytosine (C), and uracil which is written as (You). Thymine (T) may also be present along with uracil depending on the type of ribonucleic acid. Consequently, the nitrogenous bases in RNA are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine.There are two types of nitrogenous bases in any ribonucleic acid, namely -- purine and pyrimidine.
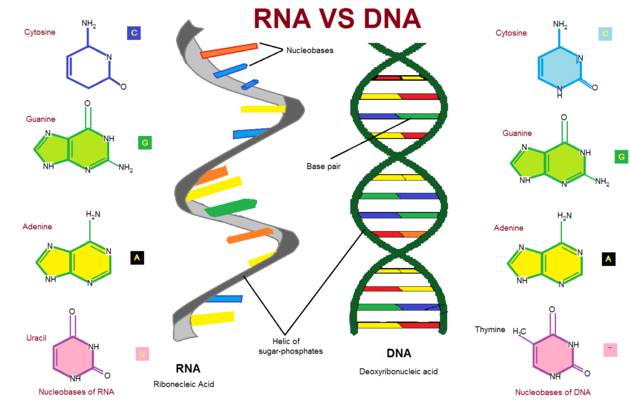
Comparison with DNA
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid which carries the genetic instruction in all living organisms. The genetic information includes growth, development, reproduction, and functioning of an organism. Like an RNA molecule, DNA is also composed of nucleotides. Slight differences exist between the nucleotides of the two, as well as in the arrangement of the molecules. Although these differences may appear subtle, they contribute towards significant functional differences in the two molecules.
The chemical structure of RNA differs from DNA in the following ways:
- 1Occasionally, RNA can be paired to form a double strand.DNA is a double-stranded helical molecule, as compared to RNA which is usually single stranded.
- 2In the nitrogenous base of DNA, thymine is paired with adenine while in RNA, the thymine is replaced by uracil.
- 3The DNA molecule contains a deoxyribose sugar as opposed to the ribose sugar found in RNA.
Synthesis of RNA
The synthesis of RNA is called transcription. As the name implied, transcription is a process of transcribing or transferring DNA nucleotide sequence information into RNA sequence information. The synthesis is catalyzed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. During the initiation of transcription, RNA polymerase unwinds a short stretch of double-helical DNA to produce a single-stranded DNA template from which it takes instructions. The enzyme then progresses in the 3′ to 5′ direction to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule.
There are different classes of RNA:
- 1Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- 2Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- 3Transfer RNA (tRNA)
- 4Small interfering RNA (siRNA)
- 5Micro RNA (miRNA)
- 6Small nuclear RNA (snRNA)
mRNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information about the protein to be synthesized to the ribosome. The ribosome is found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes and serves as the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the mRNA, thus an mRNA can be called as the architect in protein synthesis, while ribosome is the constructor.
rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is made up of two components, protein, and RNA. rRNA binds tRNA and other accessory molecules for synthesis. The RNA component of the ribosome has a catalytic function like an enzyme.
tRNA
Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another class of ribonucleic acid and acts as the middleman between mRNA and rRNA in the synthesis of protein. tRNA has two arms, with one of the arms attached to amino acids, while the other binds to the mRNA. Amino acids are carried by tRNA and connected by a peptide bond during the process of translation, to produce a protein.
miRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a non-coding RNA of 20-22 nucleotide length, that plays an important role in gene silencing. miRNA binds to mRNA, thus silencing the gene. The application of miRNA continues to be explored in biotechnology to stop the reproduction of unwanted genes in cancer therapy. The failure of miRNA to efficiently silence unwanted genes often result in the uncontrolled synthesis of the protein, which is a hallmark for cancer. Efforts are continuing to attempt to increase the activity of miRNA in cells for stricter post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression.
siRNA
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) are double-stranded RNA and contain about 19 nucleotides. siRNA, along with miRNA bind to mRNA and promotes gene silencing. While miRNA converts mRNA to 'processing bodies' which are then either stored or destroyed, the siRNA differs in that it always destroys the mRNA.
snRNA
Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) is involved in the process of gene splicing. siRNA is often found in the intron region of genes encoding proteins that are involved in the ribosome synthesis. The average length of snRNA is 150 nucleotides. The specific mechanism by which snRNA regulates RNA modification is still unknown.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Types and Structure of Ribonucleic Acid. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 23, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/Ribonucleic_Acid
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Types and Structure of Ribonucleic Acid." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/Ribonucleic_Acid Accessed 23 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Types and Structure of Ribonucleic Acid." Accessed Apr 23, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/Ribonucleic_Acid.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Biology
Recent edits by: SarMal, Marisha, Jen Moreau