Protein Synthesis
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor)
RNA
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. There are several different types, distinguished by a small letter in front of the RNA. It is similar to DNA, and is made up of nucleotides, but with a few important differences.
- It is only a single strand of nucleotides, rather than a double like DNA.
- The sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose.
- Where DNA has the base Thymine, RNA has Uracil (You).
Transcription
This is the first stage of protein synthesis, where the DNA code on a chromosome is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA)
- 1The first step is for the DNA to unwind, now RNA polymerase goes along the strand with the genetic code and catalyses the mRNA nucleotides together making a copy of the genetic sequence (like a negative in photography).Advertisement
- 2The purpose of transcription was to make a copy of the code since the DNA is the master copy and too previous to leave the nucleus.The mRNA molecules peel away from the DNA and leave the nucleus and into the cytoplasm.
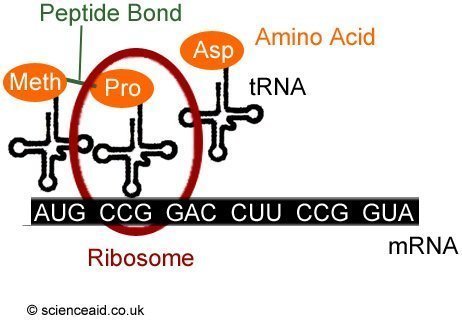
Translation
At this stage, the genetic code in the mRNA molecule is used to build a polypeptide, which can then be used for a protein or enzyme. It might even become one of the enzymes which helps in protein synthesis
Floating around in the cytoplasm are ribosomes and tRNA molecules. This tRNA is attached to a specific amino acid at the top, and at the bottom is has an anti codon.
The anti-codon is complimentary to the codon on the mRNA, for example, the first codon on the mRNA is AUG, the anti-codon on the tRNA would be UAC, which corresponds to Methionine. The ribosome moves along the mRNA systematically fusing together the amino acids it goes along. Eventually it gets to a stop codon, so the chain is complete, creating a polypeptide. These can interact in different ways to create a protein or enzyme.
Mutation
A gene mutation occurs when there is a change in the sequence of bases, such as when a gene is copied incorrectly. This can result in one or more different amino acids being incorporated into the protein. To simplify this, if the codon is supposed to be AUG, which codes for Methionine but a mutation occurs so that it reads AUC, it would be isoleucine, which changes the polypeptide and then the protein or enzyme slightly, however, it doesn't always result in a change because there are several codes for each amino acid.
There are three main types of mutations that can occur. Examples of these are in the table below.
| Original Sequence | CAT CGT AAG TGA GAC |
| Substitution | CAG CGT AAG TGA GAC |
| Addition | CAT CTG TAA GTG AGA C |
| Deletion | CATC GTA ACT GAG AC |
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Protein Synthesis. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 25, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/biology/genetics/proteinsynthesis.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Protein Synthesis." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/biology/genetics/proteinsynthesis.html Accessed 25 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Protein Synthesis." Accessed Apr 25, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/biology/genetics/proteinsynthesis.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Genetics
Recent edits by: Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)