Fungi and Yeast
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor), SmartyPants, MaxScience and 1 other
The Structure of Fungi and Yeast
The diagram above shows a typical structure of a fungus. A fungus is made of hyphae, which are long tubes. Collectively they are called mycellium and form branches that can cover many acres.
On the right, we have zoomed in on a hypha, and you can see its structure. It has all the typical features of a cell, but there are some unique aspects. The hypha is a long tube and effectively one cell. However, it could be divided into compartments by septa; the hypha has many nuclei. The tip is tapered, this is where it is growing outwards and is known as the extension zone. Fungi grow specialized areas for reproduction called fruiting bodies. These can grow very large and are visible to the naked eye, where they are known as mushrooms. It is from these that spores are produced.
Yeasts
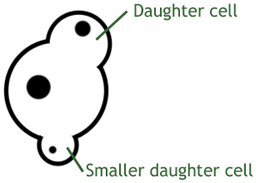
Yeasts are a type of fungi, but unlike most, they are made up of individual cells (unicellular). They reproduce by budding where little bits of new yeast grow and break off.
As a living thing, yeast respire. Unlike human anaerobic respiration where lactic acid is produced, they produce ethanol. Alcoholic drinks such are beer are made by fermenting with yeast, this produces alcohol.
Glucose ==>> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide C6H12O6 ==>> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Pathogenic Fungi
As microorganisms, fungi can be pathogenic, fungi like warm and damp environments which they can find in places like between the toes and in the vagina. Have a look at the table below to see some examples of pathogenic fungi.
| Disease | Fungus | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Athletes Foot | Trichophyton Rubrum | Athletes Foot refers to a fungal infection of the foot and can be caused by many different fungi. The mold or yeast grows on the surface and into the skin and causes itching. |
| Thrush | Candida Albicans | Thrush refers to this fungus infecting the vagina and causes itching. However, the same fungus can also infect the penis and mouth. This infection is generally known as candidiasis. It exists naturally in many people with no symptoms, but irritation of the skin, diabetes and hormone therapy can cause an outbreak. |
| Pneumonia | Histoplasma Capsulatum
Pneumocystis Jiroveci |
Pneumonia is a general term for infection and inflammation of the lungs. It is important to note that it can be caused by bacteria or virus and that fungal pneumonia is quite rare and only normally occurs in people with AIDS because of their weakened immunity. |
Fungi in Industry
Fungi have many uses in the industry that are covered in various areas of this site. They are especially useful in food.
- 1Is used in fermenting beer and wine to produce alcohol, it is also added to bread to make it rise and alter its texture.Yeast.Advertisement
- 2These are another culinary use of fungi; truffles are a fungus that is highly prized and expensive that are used in cooking.Mushrooms.
- 3Fungi can be useful for producing products in fermenters, the best example of this would be penicillin production.Penicillin.
- 4Returning to food: Quorn is a meat alternative, it is derived from the mould Fusarium venenatum. F. venenatum is grown in oxygenated water and fed glucose and various vitamins. The resulting material is removed and heat treated, bound together with egg albumen and pressed into a mince to give it a texture like meat.Quorn.
Extracellular Digestion
This is where digestion is done outside of the organism. This is seen in saprophytic fungus (saprophytic meaning decomposer). The fungi secretes the enzymes into their surrounding material and then absorbs the products. A way of measuring the activity of amylase is to have an agar plate with starch; make a small well and put in the amylase enzyme. Incubate for a time and then flood the area with iodine. It will show a clear zone where the starch has been digested. You can see which is the more effective in the diagram below.
Questions and Answers
Hi Jamie I was wondering about extracellular digestion in yeast?
Hi Jamie I was wondering about extracellular digestion in yeast and how this happens and what it means? It doesn't explain it.
Fungi is Yeast which feeds on dead organic material. Extracellular digestion is the way in which Fungi feeds. Fungi secrete enzymes through the walls of their fine feeding hyphae. This breaks the food down into nutrients. Once the nutrients are digested there reabsorbed through the hyphae wall. The nutrients are used in respiration to release energy, or they are used for growth.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Fungi and Yeast. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 20, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/biology/micro/fungiyeast.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Fungi and Yeast." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/biology/micro/fungiyeast.html Accessed 20 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Fungi and Yeast." Accessed Apr 20, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/biology/micro/fungiyeast.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Micro
Recent edits by: MaxScience, SmartyPants, Taylor (ScienceAid Editor)