Testing for Anions
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor)
Carbonate
Ion CO32-, carbonate is found in limestone, or calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
To test for it, you must first: Add a dilute acid to the sample. A gas is given off which when tested should prove to be carbon dioxide.
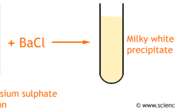
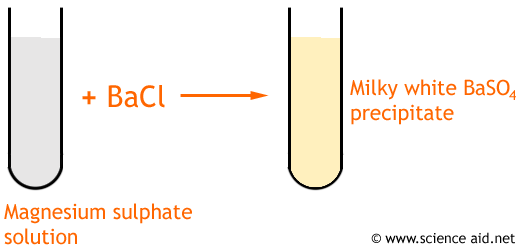
Sulphate and Sulphide
Sulphate is SO42- and Sulphide is SO32-
By adding barium chloride to the solution you are testing, a white precipitate will form. If you add hydrochloric acid, the sulphate (SO42-) WILL NOT dissolve and the sulphite (SO32-) will.
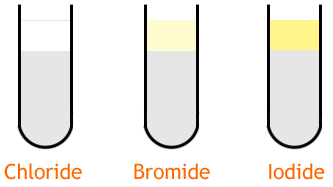
Halogen Tests
The test for halogens, or halide ions, is to add silver nitrate to a solution. Often, nitric acid is added first as well. If there are chloride, bromide or iodide ions in the solution they will react with silver to form a precipitate. The different precipitates are summarized in the table below.
The ionic equations for these reactions are:
- 1Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) ==>> AgCl (s)Advertisement
- 2Ag+ (aq) + Br- (aq) ==>> AgBr (aq)
- 3Ag+ (aq) + I- (aq)==>> AgI (aq)
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Testing for Anions. (2016). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 19, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/testanions.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Testing for Anions." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/testanions.html Accessed 19 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Testing for Anions." Accessed Apr 19, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/testanions.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Applied
Recent edits by: Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)