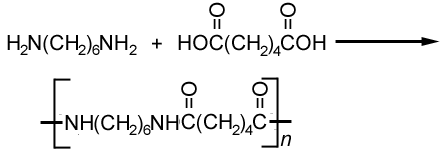Polymers
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor)
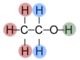
A polymer is a large molecule made up of lots of small molecules. In the natural world, fats and proteins are polymers. A monomer is the name for the small molecule that is part of the chain, in the following example, the monomer is ethene.
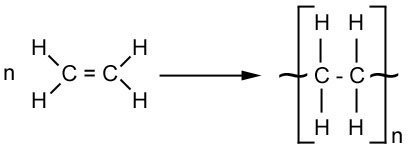
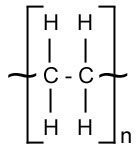
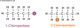
Making Polythene
The monomers are passed over a heated catalyst and polymerization occurs. In this example a long chain of molecules called poly(ethene) or polythene is made.
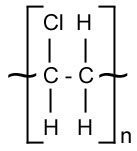
NB: The molecule in square brackets shows the structure of each monomer, and the lines coming out show how they are bonded to each other. The letter n denotes that the sequence is repeated many times.
Addition Polymers
Addition polymerization is the creation of polymers from monomers containing a C=C bond. As the name suggests it is an addition reaction, and is written as follows:
- The above diagram shows the formation of polystyrene, however, many groups could be attached to the C=C, with 4 Fluorenes, Teflon would be made that way.
- And a single methyl group results in polypropene (polypropylene).
- Polyalkenes are made by the addition polymerization of alkenes. They contain many carbon bonds, which means there is little bond polarity and they are therefore inert which means they are not biodegradable.
Condensation Polymers
Condensation polymers are formed by the reaction of molecules with two functional groups, and produces water as a by-product.
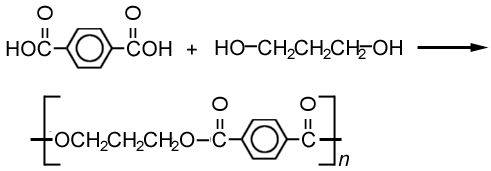
- 1The first example is the formation of polyesters by the reactions of dicarboxylic acids and diols, forming ester links. For example, in the production of Terylene.Polyesters.Advertisement
- 2is another polyester formed by condensation. It is formed by the reaction of dicarboxylic acids and diamines. This is how Nylon-6,6 is made.Polyamide.
Unlike addition polymers, polyamides and polyesters are biodegradable and can be broken into their constituent molecules by hydrolysis, where water is added to the polymer.
Uses and Others
Polymers are very useful, and are used to replace traditional materials like metals, paper and rubber. The following table shows some other polymers along with their uses.
| Name | Structure | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Poly(ethene)
Polythene |
Plastic Bags Plastic film Sheets |
|
| Polypropene
Propathene |
Crates Rope Carpet |
|
| Polychloroethene
PVC |
Waterproof material Insulating wire Guttering |
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Polymers. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 25, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/polymers.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Polymers." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/polymers.html Accessed 25 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Polymers." Accessed Apr 25, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/polymers.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Organic
Recent edits by: Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)