Electrolysis
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor), Jen Moreau, Doug Collins and 3 others
Electrolysis of Brine
Brine is merely sodium chloride (NaCl), dissolved in water.
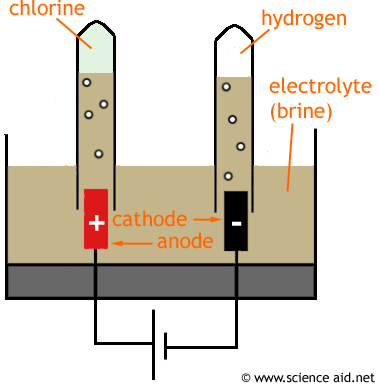
If you perform electrolysis on brine you will get three substances: chlorine, hydrogen and sodium hydroxide.
The cations move towards the cathode. So H+ and Na+ will go this way. The hydrogen gas bubbles up and is collected in the test tube. Pairs of H+ ions will from H2 molecules.
The anions move towards the anode. Cl- is collected in the test tube - it becomes Cl2 molecules, OH - also moves in this direction.
When the current is stopped the Na+ and OH- have no force holding them to their respective electrodes, so they will form ionic bonds together, making sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Testing
To test for hydrogen you first take the test tube, then seal it. Now you get a wooden splint or match and light it. Quickly unseal the test tube and drop the splint in. You should hear a 'pop' sound as the hydrogen combusts in a rapidly exothermic reaction.
To test for chlorine you do the same as with hydrogen, but instead of a match, you drop a damp piece of litmus paper into the test tube. It should turn white because the chlorine has bleached it.
Sodium hydroxide is an alkaline solution, so you can use one of the tests you know for that. Turning litmus paper purple or universal indicator turns the solution blue.
Uses
This electrolysis process is very useful in the world of industry because the products have a lot of uses, as well as the combinations of some of the products as well. The table below outlines some of the products that rely on the electrolysis of brine.
| Compound | Uses |
|---|---|
| Chlorine: | PVC, pesticides; water treatment |
| Hydrogen: | Fuel, margarine |
| Sodium hydroxide: | Soaps and detergents, paper, food products |
| Sodium chlorate. | Sodium hydroxide and chlorine are reacted together to form this which is used in household bleach. |
Questions and Answers
Why did I get more H2 than Cl2 in brine electrolysis?
Hi, I did electrolysis of salted water (from tap water) in a Hoffman Voltameter with graphite electrodes (10V). There is much more H2 produced than Cl2. What might be the cause? Also, after stopping the electrolysis, the positive electrode seems to start dissolute into the solution.
I assume the reason behind having more H2 and electrode dissolution can be related to the composition of tap water. Tap water contains some salts and particularly chloride ions that may undergo other redox reactions at an electrode. These redox reactions produce newer solutes, that can either react with each other forming newer products or can change the results of your experiment. This is most probably what has happened in your experiment. Other reactions have occurred that increased the concentration of H2 more than the Cl2 and the different solutes formed reacted at the positive electrode.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Electrolysis. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 17, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/electrolysis.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Electrolysis." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/electrolysis.html Accessed 17 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Electrolysis." Accessed Apr 17, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/applied/electrolysis.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Applied
Recent edits by: vcdanht, SmartyPants, Doug Collins