Epoxyethane
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Jen Moreau
Epoxyethane
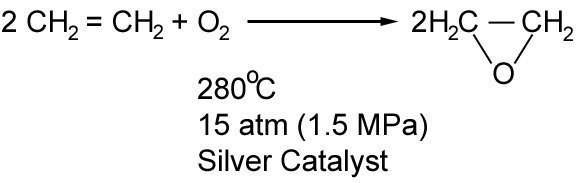
Production of Epoxyethane
Epoxyethane also known as ethylene oxide, is produced industrially by the above reaction. This manufacturing process is very hazardous, firstly because epoxyethane is poisonous and carcinogenic (causes cancer), and secondly because it is very explosive upon contact with air.
Properties
Epoxyethane is very reactive because of its structure. The ring between the two carbons and oxygen is very strained and the bond angle is forced to be much smaller than is normal in carbon. This means that it is very reactive; and the carbon-oxygen bond is also broken in reactions.
Uses
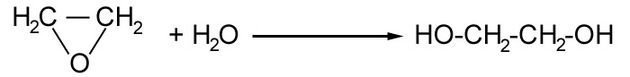
Epoxyethane is reacted in water with a catalyst of a very dilute acid and at a moderate temperature in the following reaction.
This reaction produces a diol, which means it has two OH alcohol groups. This reaction is of industrial importance because ethane-1,2-diol is used as car antifreeze and also in the production of polyesters.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Epoxyethane. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 26, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/epoxyethane.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Epoxyethane." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/epoxyethane.html Accessed 26 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Epoxyethane." Accessed Apr 26, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/chemistry/organic/epoxyethane.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Organic
Recent edits by: Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)