Osmosis
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor), vcdanht
About Osmosis
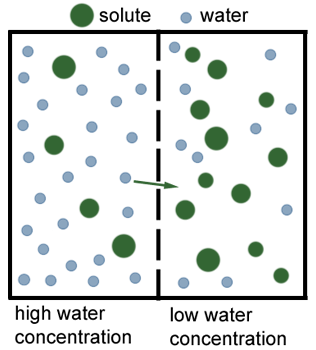
We already know what diffusion is, and osmosis is simply a special type of diffusion, where only some molecules can move because they can pass through a partially permeable membrane:
The left has a high concentration of water and the right a low concentration. By diffusion, water will naturally level out and pass through the membrane. The solute, however will not be able to diffuse, as they can't fit through the membrane.
Therefore we define osmosis as: the net movement of water from a dilute to a concentrated solution, through a partially permeable membrane.
Turgidity
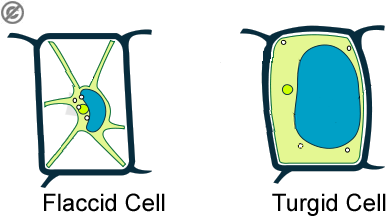
Osmosis plays an important role in maintaining the turgidity of cells. If they are in a solution of distilled water for example, the cell will take on more water molecules without losing the precious nutrients. And become turgid
If, on the other hand, you surround the cell with a highly concentrated glucose solution, there will be a net movement of water molecules away from the cell. Therefore the cell will become floppy and flaccid.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Osmosis. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 28, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/biology/cell/osmosis.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Osmosis." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/biology/cell/osmosis.html Accessed 28 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Osmosis." Accessed Apr 28, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/biology/cell/osmosis.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Cell
Recent edits by: Taylor (ScienceAid Editor), Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)