Minority Influence and Compliance
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Taylor (ScienceAid Editor)
These two topics are similar, but it is very important that you do not confuse the two since there is a difference.
- 1This involves a minority persuading the majority regarding a particular opinion.Minority Influence.Advertisement
- 2This involves someone persuading you to agree to do something (usually buy their product).Compliance.
Minority Influence Study: Moscovici and Nemeth
The research into conformity has been focused on majority, and the effects of the minorities have been neglected.
| Aim | To discover how a minority affects a majority, depending on where they sit. |
| Method |
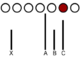
Groups of 5 people (including one confederate) were asked to make jury-style decisions. The confederate was either assigned to, or chose A, B, or C (see below). They also had to take a minority view. |
| Results | Little influence when assigned to any seat. But when the confederate chose where to sit; position C was very influential. |
| Conclusion | Minority influence is more likely when one is the focus of attention. |
| Evaluation | This experiment has good ecological validity, as making decisions in a group is the sort of task that someone commonly encounters in their life. |
Factors
Through research such as that described above, and others, Moscovici (1985) concluded minority influence was more likely under the following conditions.
- 1The opinion expressed must remain the same.Consistency.
- 2The minority must not appear too rigid and dogmatic.Flexibility.
- 3If the minority shows itself dedicated to the issue, then conversion may result (where someone comes over to your cause), rather than compliance.Commitment.
- 4The position must be consistent with social trends.Relevance.
Compliance
Compliance is getting other people to agree with a request. This is different from conformity, because it relates to a specific thing. An example would be salespeople selling door-to-door, or in a shop.
Techniques for Gaining Compliance
Techniques for gaining compliance are based on the following things.
- 1Compliance is more likely when we think something is in short supply. For example, if you are told a shop only has one or two of the items left in stock, you will be more likely to buy it.Scarcity.
- 2If someone is our friend or we like them, compliance is more likely.Friendship.
- 3This is if we think we should do something. For example, we may be more likely to donate to charity because it is perceived as something we should do.Social Validation.
- 4Compliance is more likely with an authoritative figure. It is important that you do not confuse this with obedience.Authority.
- 5If you owe a favour to someone, i.e they've already done something for you, you are apt to be more compliant. An example: If you go into a car salesroom and look interested, the salesperson may give you a warm drink, or if you are considering buying something very expensive they may take you out to dinner, etc. These are methods employed to make you more compliant.Reciprocity.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Minority Influence and Compliance. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 26, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/psychology/social/minority.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Minority Influence and Compliance." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/psychology/social/minority.html Accessed 26 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Minority Influence and Compliance." Accessed Apr 26, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/psychology/social/minority.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Social
Recent edits by: Jamie (ScienceAid Editor)