Biotechnology: Screening Procedures, Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin, Industrial Enzymes
Edited by Jamie (ScienceAid Editor), Jen Moreau, SmartyPants, Sharingknowledge and 1 other
- 1 Screening Procedures
- 2 Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin
- 3 Recovering Penicillin: Downstream Process
- 4 Industrial Enzymes
-
5 Questions and Answers
- 5.1 Can you explain the downstream process of penicillin??
- 5.2 Discuss how microorganisms are screened for use in the food production process?
- 5.3 Which fermentor used penicillin production and what does are the production strain details?
- 5.4 What part of the antibiotic process involves biotechnology?
- 5.5 Explain how microbes would be screened to show they produced a protease enzyme. Consider how you could determine the different optimum growth conditions that the microbe would require?
- 6 Referencing this Article
- 7 Comments
Screening Procedures
Micro-organisms are used in industry for a large number of processes. This is because they have simpler nutrient requirements, fast growth rates and can be genetically manipulated. Before using micro-organisms, they must be screened to find the most suitable for a particular process.
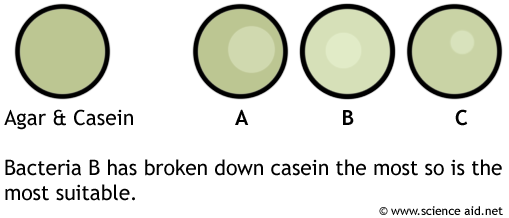
For example, fungi can be grown with several bacteria to see if they have any antibiotic effect. Similarly, bacteria can be screened for protease production. Agar plates are treated with casein - a protein that makes it cloudy. If the bacteria produce protease, a clear area where the casein has been hydrolyzed will form; the larger this area is, the higher the concentration of protease that has been produced.
Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin
For detail on the fermenter see fermentation.
There are two types of culturing techniques used to grow large amounts of micro-organism. Batch culturing has all substrates added together are the start and the products harvested at the end. The cells are in the exponential growth for a smaller period and the amount of product is limited by the initial amount of substrate. This means batch culturing is less productive but contamination is less likely. Sometimes it is necessary to use batch culturing: bacteria or fungus will not produce antibiotic in the exponential phase because there isn't much competition.
Another process is continuous culture where a new substrate is continually added and product continually harvested. In this method, the cells are maintained in the exponential growth phase. It makes a lot of product and once you have got the conditions right, is automatic. However, the fermenter can only be used for one product and contamination is more likely.
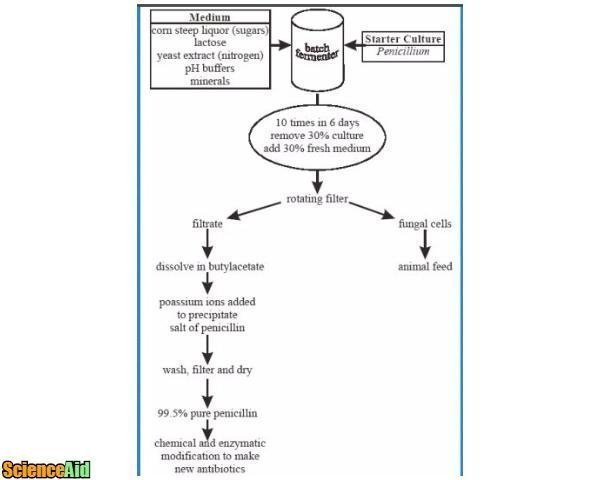
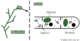
The products of fermentation are not usually purely what you want (notable exceptions are in food production: beer, yogurt etc). So downstream processing is carried out to extract purified product, as is the case in Penicillin production (stages 3, 4 & 5 in the diagram below).
The antibiotic Penicillin is obtained from a strain of the mould Penicillium chrysogenum. It is fermented in a batch culture as if the P. chrysogenum is kept in the exponential phase it uses the energy to grow rather than make Penicillin.
The main stages of Penicillin production are:
Recovering Penicillin: Downstream Process
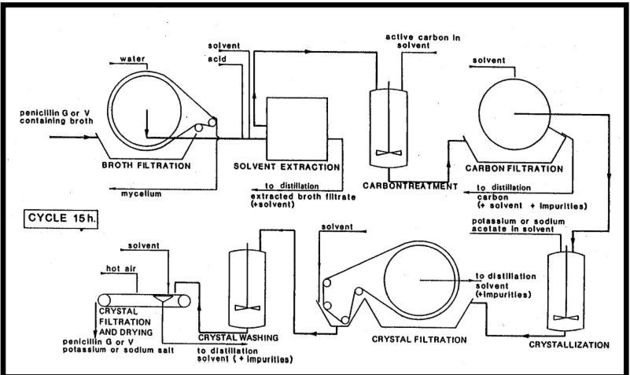
Because penicillin is produced naturally by fungi after fermentation penicillin must be flushed of any impurities. Downstream processing purifies the end product and ensures the penicillin produced is as pure and healthy as possible. There are ten steps to the downstream processing of penicillin:
- 1Broth filtration.Advertisement
- 2Filtrate cooling.
- 3Additional filtration.
- 4Penicillin extraction.
- 5Treatment with carbon.
- 6Aqueous transfer.
- 7Recovery of solvent.
- 8Crystallization.
- 9Washing of crystals.
- 10
The downstream process used today is similar to the process used by Fleming when he first began producing penicillin. However, since Fleming's production, researchers and scientists have taken steps in perfecting the downstream process of penicillin. Because of the global dependence on penicillin, researchers and scientists continue to try new technologies and create a better process that will increase production, yield and quality assurance of penicillin production.
Industrial Enzymes
Micro-organisms can be used to produce enzymes that are useful in certain industrial applications. A more efficient method of using them is to isolate an enzyme and use it by itself. This is better because higher concentrations of an enzyme can be obtained and only one reaction is taking place - whereas using whole micro-organisms would have numerous enzyme reactions and more products to process.
A further problem is encountered in that enzymes are expensive to produce. This is solved by reusing the enzyme, this is made possible by immobilizing the enzymes, this way they do not contaminate the end products are can be reused.
Some methods of immobilizing an enzyme are:
| Method | How it works | Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding with a cross-linking agent. | Enzymes are linked to each other by chemical bonds. They may all be joined by amino acids for instance. | |
| Entrapment inside a gel. | Enzyme is trapped in an inert 'matrix' such as alginate or collagen, and cannot be washed out. Substrates and products, though, may diffuse in and out of the matrix. This type of enzyme takes the form of small beads. | |
| Binding to an adsorbing agent. | A support matrix (glass beads or carbon) has enzymes attached to it by weak forces (a bit like magnetism). The adsorption may alter the shape of the enzyme, though, and the force might be too weak to hold the enzymes in place very strongly. |
Questions and Answers
Can you explain the downstream process of penicillin??
Please see the newly added section "Recovering Penicillin: The Downstream Process"
Discuss how microorganisms are screened for use in the food production process?
See the new article Using Microorganisms in Food Production all about microorganisms in food production.
Which fermentor used penicillin production and what does are the production strain details?
Please give the full details about production strain for penicillin production in pdf format. I prefer a seminar so I have full details about penicillin production
During the World War II in 1928, penicillin has been discovered and leads to the development of antibiotics and provided great impact in the world of biotechnology. The production of penicillin is done through the process of fermentation.
This method is done aseptically in stainless steel tank reactors that have a capacity of 30-100 thousand gallons. This process involves several growth phases. It usually takes 2-3 seed phase and then followed by the production phase that takes 120 to 200 hours.
Glucose, sucrose and other forms of crude sugars which are examples of carbon have been used in this process. 65% of this carbon is being used for cellular maintenance, 25% is used for the growth and 10% for the penicillin production. This sugar can also useful in regulating the pH value of the penicillin during its the production phase.
To remove an amount of fermentor contents and replace it with a fresh sterile medium, mini harvest protocol is being obtained. This process can be repeated to enhance the penicillin yield per fermentor without reducing its yield. Then penicillin is extracted into a medium and recovered at the end of the fermentation process.
Penicillin production strains:
During the Second World War, the traditional process of penicillin production provides one milligram per cubic decimeter but later production with the aid of different species like penicillium chrysogenum and the development of extraction procedures the production yields to 50 grams per cubic decimeter.
The production of penicillin can still be improved through the improvement of the composition medium by removing the Penicillium Chrysogenum that grows better in the large deep fermentation tank and by continuous improvement of culture technique for the cultivation of molds in a large volume of liquid medium that must be kept with sterile air into it.
One of most significant thing in high-yielding Penicillin chrysogenum strain is the amplification of the penicillin biosynthetic gene cluster and molecular strategies involving an increase in biosynthesis gene has also been developed.
The need for the penicillin for therapeutic purposes is still at its peak however the laboratories in the United Kingdom were not able to provide enough resources to improve the production industries of penicillin during the World War II.In 1941, Howard Florey and Norman Heatley go to the US to work with the scientist in U.S Department of Agriculture's Northern Regional Research Laboratory (NRRL) in Peoria IL and with some British and American scientist for the improvement of the production of penicillin.They were able to identify the strains of the Penicillium chrysogenum that produce the highest levels of penicillin that is usually obtained from a moldy cantaloupe in a Peoria farmer's market. They used x-rays and ultraviolet light to create higher penicillin-producing mutants. Through their study, they were able to reveal the improvement of growing penicillin through submerging the culture media rather than on a plate surface because of the changes in the nutrient base from sucrose to lactose. This breakthrough was able to save thousands of lives during the World War II.
What part of the antibiotic process involves biotechnology?
Antibiotics are created using biotechnology. Antibiotics are created organically by microorganisms. In order to create the massive amount of antibiotics required, biotechnologists grow, cultivate and use the microorganisms. For example, fungi are often used in antibiotics, so biotechnologists are able to grow healthy fungi cells free of mutations to be used in antibiotics.
Explain how microbes would be screened to show they produced a protease enzyme. Consider how you could determine the different optimum growth conditions that the microbe would require?
Explain how microbes would be screened to show they produced a protease enzyme. Consider how you could determine the different optimum growth conditions that the microbe would require. Describe how the growth of the microbe could be scaled up to produce large quantities of protease enzyme.practical investigating the effect of temperature on the growth rate of E.coli. Explain the results and support with data from the practical. the practical investigating the effect of pH on the growth rate of S.albus. Explain the results and support with data from the practical
ScienceAid QnA. This section is not written yet. Want to join in? Click EDIT to write this answer.
Referencing this Article
If you need to reference this article in your work, you can copy-paste the following depending on your required format:
APA (American Psychological Association)
Biotechnology: Screening Procedures, Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin, Industrial Enzymes. (2017). In ScienceAid. Retrieved Apr 26, 2024, from https://scienceaid.net/biology/micro/biotechnology.html
MLA (Modern Language Association) "Biotechnology: Screening Procedures, Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin, Industrial Enzymes." ScienceAid, scienceaid.net/biology/micro/biotechnology.html Accessed 26 Apr 2024.
Chicago / Turabian ScienceAid.net. "Biotechnology: Screening Procedures, Fermentation and the Production of Penicillin, Industrial Enzymes." Accessed Apr 26, 2024. https://scienceaid.net/biology/micro/biotechnology.html.
If you have problems with any of the steps in this article, please ask a question for more help, or post in the comments section below.
Comments
Article Info
Categories : Micro
Recent edits by: Sharingknowledge, SmartyPants, Jen Moreau